
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 1-2 Question Answer Solved worksheets | Curiosity is essential for young learners to build a strong foundation in the subject, and NCERT Class 6 Science Question Answer. Understanding the chapter thoroughly helps students grasp key concepts, improve comprehension, and perform well in exams.
In this post, NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 1-2 Question Answer Solved | Curiosity, we provide detailed NCERT Class 6 Science Question Answer to make learning easier and more effective. Whether you are a student looking for well-explained solutions or a parent guiding your child, this guide will be a helpful resource for mastering the chapter with confidence. Also, we include NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 1-5 Question Answer Meaning in Bengali.
Table of Contents
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 1-2 Question Answer Solved | Curiosity | Must Read
Chapter 1: The Wonderful World of Science (NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science)
Activity 1.1: Let us think and write (NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science)
1. Write about a similar problem that you tried to solve.
Ans: You can write this answer this way.
One day, my toy car stopped moving. I had just played with it the day before, and it was working fine. I was curious to know what went wrong.
2. What steps did you take?
Ans: First, I checked if the car was switched on. It was. Then I guessed that maybe the batteries were dead. I opened the battery cover and saw that the batteries were old. I changed them with new ones, and the car started working again! If that didn’t work, I was going to check the wheels or the motor next.
Activity 1.2: Let us think and write (NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science)
1. Describe a daily life situation where you think someone was following a scientific method.
Ans: One day, my mother saw that the rice was not cooking properly. She guessed that maybe there was not enough water in the pot. She opened the lid and checked. Yes, the water had dried up! Then she added some more water and kept it on the stove again. After some time, the rice was cooked nicely. She asked a question, made a guess, tested it, and solved the problem—just like in science.
Activity 1.3: Let us think and write (NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science)
1. If you have to ask “Why?” about something, what would you ask about?
Ans: I would ask, “Why do stars twinkle at night?” I look at the sky and see them shining and blinking, and I really want to know why they don’t just shine steadily like bulbs. It makes me curious every time I see them.
2. Try to write down how you would attempt to find an answer to your question.
Ans: First, I would ask my teacher or parents if they know why stars twinkle. Then, I would look in my science book to see if it explains it. If I still want to know more, I would search for the answer on a children’s science website or watch a video about stars. I would try to understand what makes the stars look like they are blinking.
Chapter Wise NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Curiosity
| Chapter Name | Solution Link |
|---|---|
| 1. NCERT Solutions for Class 6 science Chapter 1 (The wonderful world of science) | Visit Here |
| 2. NCERT Solutions for Class 6 science Chapter 2 (Diversity in the living world) | Visit Here |
| 3. NCERT Solutions for Class 6 science Chapter 3 (Mindful Eating) | Visit Here |
| 4. NCERT Solutions for Class 6 science Chapter 4 (Exploring Magnets) | Visit Here |
| 5. NCERT Solutions for Class 6 science Chapter 5 | Coming Soon |
Chapter 2: Diversity in the Living World (NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science)

Activity 2.1: Let us explore and record (NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science)
1. Plan a nature walk with your teacher to a park or a nearby forest.
Ans: If you have any idea about the nature walk plan, then you can answer this question by yourself. Otherwise, I am here to help you.
Nature Walk Plan
- Where we will go: We will go to a nearby park or forest with our teacher. It is a clean and green place with many trees, birds, and animals.
- Who will go: Our science teacher will take us. All students of our class will join. We may also invite a nature expert or an elder who knows about plants and animals.
- When we will go: We will go in the morning when the weather is cool.
- What we will carry: a notebook and pen, a water bottle, a cap or hat, and a magnifying glass or binoculars.
- What we will do: Look at different types of plants and trees, Try to spot birds, butterflies, and monkeys. talk to our teacher and ask questions.
- Rules to follow: Don’t touch or harm any plant or animal, don’t litter in the park, help each other, and stay together.
- After the walk: we will return to school, share what we saw and learned with the class, and make a nature wall or chart with our notes and drawings.
2. While on the nature walk, observe different plants, insects, birds, and other animals. Also, note the weather conditions, whether it is hot, cold, windy, and so on.
Ans: You can write the answer to this question in this way. I am providing an answer format for this question.
Nature Walk Observations
Date:
Time:
Place:
Teacher’s Name:
Weather Conditions:
Temperature: hot / cold
Wind: windy / calm
Sky: sunny / cloudy / rainy
Smell: yes / no
Plants I Saw:
Small Plants:
Bushes:
Trees:
Any plants with flowers or fruits:
Insects I Noticed:
Name of the insects:
Birds I Observed:
Bird name or colour:
Did it make any sound:
Describe the sound:
Other Animals I Saw:
Here, write the animal names:
What I Liked the Most:
Write what you liked the most.
My Feelings After the Walk:
Write what you feel after the walk.
3. You can collect different types of fallen leaves or flowers and create a scrapbook.
Ans:
| Fallen Leaves to Collect | Fallen Flowers to Collect |
|---|---|
| Maple leaf | Hibicus |
| Neem leaf | Marigold |
| Mango leaf | Rose |
| Teak leave | Sunflower Petals |
| Guava Heal | Lotus |
4. What similarities and differences did you find among the plants that you observed?
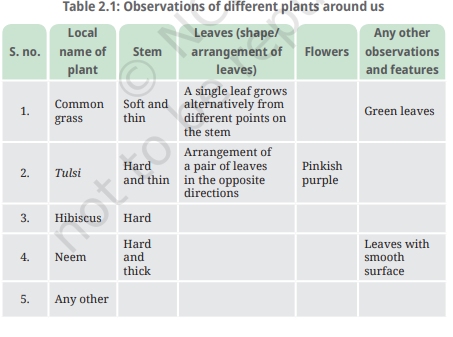
Ans:
Similarities:
1. All plants have stems.
2. Leaves are present on all plants
3. Green leaves
Differences:
1. Stem texture.
2. Leaves arrangement and shape
3. Flowers
5. What are the similarities and differences among the animals that you have observed and recorded in Table 2.2?
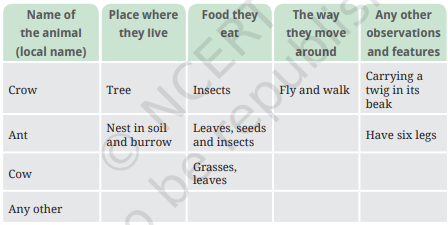
Ans:
Similarities:
1. All animals need food to survive.
2. They all have specific habitats.
3. Each animal has a unique way of moving.
Differences:
1. They have different places where they live.
2. The legs of the animals are different.
Activity 2.2: Let us appreciate (NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science)
1. Close your eyes for 30 seconds and think of one plant and one animal that you have closely observed and
appreciated very much.
Now each one of you can draw the plant and animal that you thought of on the blackboard.
What are your observations about the various plants and animals that have been drawn?
Ans:
Plant I thought of: Sunflower
Animal I thought of: Squirrel
You can draw the images of what you thought.
Observations about various plants and animals that have been drawn.
Plants:
- Different shapes and sizes of leaves.
- Some plants had bright flowers (like hibiscus and rose), while others were leafy.
- Stem types varied — some were soft and green, while others were hard and woody.
- A few drawings showed fruits growing on plants, showing how they are also sources of food.
Animals:
- Movement styles differed — some animals fly (birds), some walk (dogs, cows), and some crawl (snakes).
- Animals had different body parts — wings, tails, horns, beaks, etc.
- Some animals were domestic (cow, dog, cat), and some were wild (lion, deer).
Chapter Wise NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Curiosity
| Chapter Name | Solution Link |
|---|---|
| 1. NCERT Solutions for Class 6 science Chapter 1 (The wonderful world of science) | Visit Here |
| 2. NCERT Solutions for Class 6 science Chapter 2 (Diversity in the living world) | Visit Here |
| 3. NCERT Solutions for Class 6 science Chapter 3 (Mindful Eating) | Visit Here |
| 4. NCERT Solutions for Class 6 science Chapter 4 (Exploring Magnets) | Visit Here |
| 5. NCERT Solutions for Class 6 science Chapter 5 | Coming Soon |
Let Us Enhance Our Learning (NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science)
1. Here are two types of seeds. What differences do you find among the roots and leaf venation of their plants?
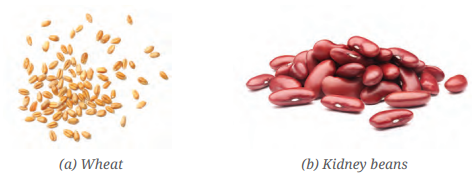
Ans:
| Feature | Wheat | Kidney beans |
|---|---|---|
| Type of seed | Monocot | Dicot |
| Root type | Fibrous root | Taproot |
| Leaf venation | Parallel venation | Reticulate venation |
2. Names of some animals are given below. Group them based on their habitats. Write the names of aquatic animals in the area marked ‘A’ and terrestrial animals in the area marked ‘B’. Enter the names of animals living in both habitats in part ‘C’.
Horse, Dolphin, Frog, Sheep, Crocodile, Squirrel, Whale, Earthworm, Pigeon, Tortoise
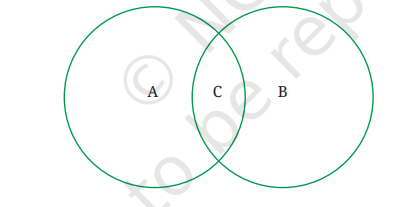
Ans:
Aquatic Animals: Dolphin, Whale
Terrestrial Animal: Horse, Sheep, Squirrel, Earthworm, pigeon
Amphibious Animal: Frog, Crocodile, Tortoise
3. Manu’s mother maintains a kitchen garden. One day, she was digging out radish from the soil. She told Manu that radish is a kind of root. Examine a radish and write what type of root it is. What type of venation would you observe in the leaves of radish plant?
Ans:
Type of Root: Radish is a taproot. It is a thick, main root that grows deep into the soil. The part we eat is the swollen taproot.
Type of Leaf Venation: Radish leaves have reticulate venation, which means the veins form a net-like pattern on the leaf surface.
4. Look at the image of a mountain goat and a goat found in the plains. Point out the similarities and differences between them. What are the reasons for these differences?

Ans:
Similarities:
- Both are goats (same species group).
- Both have four legs and two horns.
- Both are herbivores (eat plants).
- Both have hooves and fur-covered bodies.
Differences:
| Feature | Mountain Goat | Plain Goat |
|---|---|---|
| Body Build | Sturdy and muscular (for climbing) | Slimmer body |
| Habitat | Cold, mountainous areas | Warm plains and rural areas |
| Feet | Strong hooves with better grip for rocks | Normal hooves suited for flat land |
| Color | Usually white or light-colored | Often brown, black, or mixed colors |
Reasons for differences:
- Mountain Goat – Adapted to cold climates with thick fur for warmth and strong hooves for climbing rocky terrain.
- Plain Goat – Lives in warmer areas, so has shorter fur and simpler hooves as it moves on flat ground.
5. Group the following animals into two groups based on any feature other than those discussed in the chapter— cow, cockroach, pigeon, bat, tortoise, whale, fish, grasshopper, lizard.
Ans: can group the animals based on a new feature: Ability to fly vs Cannot fly
| Ability to fly | Cannot Fly |
|---|---|
| cockroach, pigeon, bat, grasshopper | cow, tortoise, whale, fish, lizard |
6. As the population grows and people want more comfortable lives, forests are being cut down to meet various needs. How can this affect our surroundings? How do you think we can address this challenge?
Ans:
How cutting forests affects our surroundings:
- Animals lose their homes – Many animals live in forests. When trees are cut, they have nowhere to go.
- Soil gets washed away – Trees hold the soil together. Without trees, the soil gets washed away by rain.
- Less rain – Trees help in bringing rain. If we cut too many trees, it may not rain properly.
- Air becomes dirty – Trees clean the air and give us oxygen. Cutting them makes the air dirty and bad to breathe.
- Weather becomes too hot – Trees keep the weather cool. Without them, the Earth gets hotter.
What we can do:
- Plant more trees – For every tree cut, we should plant more trees.
- Use less paper – Save paper so fewer trees are cut.
- Tell others to save trees – We should tell our friends and family how important trees are.
- Don’t waste things – If we use only what we need, we won’t have to cut so many trees.
7. Analyse the flowchart. What can be examples of ‘A’ and ‘B’?

Ans: ‘A’ should be Mango and ‘B’ should be Banana.
8. Raj argues with his friend Sanjay that “Gudhal (hibiscus) plant is a shrub.” What questions can Sanjay ask for clarification?
Ans: Sanjay can ask Raj some thoughtful questions like:
- What do you mean by a shrub?
- Does the Gudhal plant have a single main stem or many thin branches from the base?
- How tall does the Gudhal plant grow?
- Is the stem of the Gudhal plant hard or soft?
- Have you seen where Gudhal is usually planted—garden, pot, or forest?
9. Based on the information in the table, find out examples of these plants for each group.
(a) What other similarities do plants of group A have?
(b) What other similarities do plants of group B have?
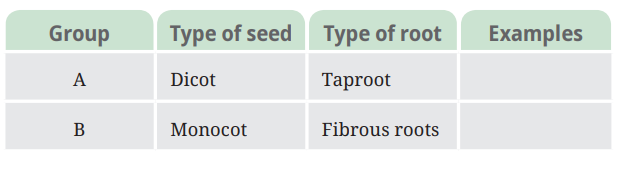
Ans: Examples of group A will be – Bean, Mango, Neem. and examples of group B will be – Wheat, Rice, Onion.
Similarities of group A plants:
- Leaves show reticulate venation.
- Flowers mostly have 4 or 5 petals.
- Seed splits into two parts.
- Stronger and deeper taproot system.
Similarities of group B plants:
- Leaves show parallel venation.
- Flowers mostly have 3 petals or multiples of 3.
- Seed has only one part.
- Fibrous root system
10. Observe the labelled part of a duck in the picture given below. What differences do you observe in the feet of the duck compared to the other birds? Which activity would the duck be able to perform using this part?
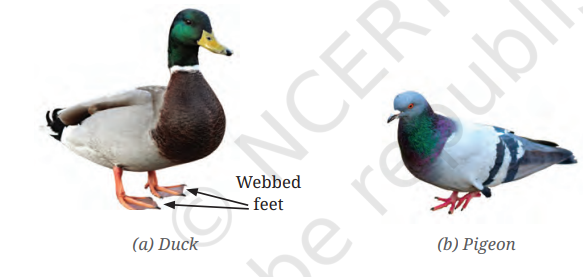
Ans: We observed that there is a majore differences in the feet.
Differences in the feet:
- Duck: Has webbed feet, which means the toes are connected by a skin-like membrane.
- Pigeon: Has clawed feet with separated toes, suitable for perching on trees or ledges.
Activity the Duck Can Perform::
- The duck can swim easily in water.
- Webbed feet act like paddles, helping the duck push water backward and move forward smoothly.
| Chapter Name | Solution Link |
|---|---|
| 1. NCERT Solutions for Class 6 science Chapter 1 (The wonderful world of science) | Visit Here |
| 2. NCERT Solutions for Class 6 science Chapter 2 (Diversity in the living world) | Visit Here |
| 3. NCERT Solutions for Class 6 science Chapter 3 (Mindful Eating) | Visit Here |
| 4. NCERT Solutions for Class 6 science Chapter 4 (Exploring Magnets) | Visit Here |
| 5. NCERT Solutions for Class 6 science Chapter 5 | Coming Soon |

3 thoughts on “NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Science | Curiosity | Solved Question Answer | Ultimate Guide 2025”