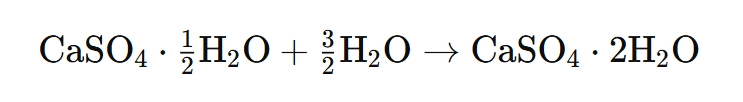Acid Base And Salt Class 10 Notes are one of the most important study resources for students preparing for CBSE Class 10 Science exams. The chapter on NCERT | acids bases and salts forms the foundation for understanding chemical reactions, the pH scale, indicators, salts in daily life, and their industrial applications.
In acids bases and salts class 10, students often find it challenging to remember definitions, formulas, chemical properties, and reactions. That’s why having well-structured and easy-to-understand notes is essential for quick revision and exam success. In this article, you will get clear explanations, key points, and reaction equations, along with an acid base and salt notes PDF that helps you revise anytime, anywhere, and score better marks in your board examinations.
CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 2 Acids Bases and Salts Pdf free download is part of Class 10 Science Notes for Quick Revision. Here we have given NCERT Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 2 Acids Bases and Salts. According to new CBSE Exam Pattern, MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science pdf Carries 20 Marks
- Introduction: (Acid Base And Salt Class 10 Notes)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Questions: Page -18
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Questions: Page – 22
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Questions: Page – 25
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Questions: Page – 28
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Questions: Page – 33
NCERT | Acid Base And Salt Class 10 Notes – Free PDF download | Must Read
Introduction: (Acid Base And Salt Class 10 Notes)
Elements combine to form numerous compounds. On the basis of their chemical properties, compounds
can be classified into three categories:
- Acids
- Bases
- Salts
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Questions: Page -18
1. You have been provided with three test tubes. One of them contains distilled water and the other two contain an acidic solution and a basic solution, respectively. If you are given only red litmus paper, how will you identify the contents of each test tube?
Answer: Take a strip of red litmus paper and dip it one by one into the solutions present in the three test tubes.
- The test tube in which the red litmus paper turns blue contains the basic solution.
- The test tube in which the red litmus paper shows no change and remains red contains the acidic solution.
- The remaining test tube, in which the red litmus paper shows no change and does not turn blue, but after comparison does not show acidic or basic behavior, contains distilled water.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Questions: Page – 22
1. Why should curd and sour substances not be kept in brass and copper vessels?
Answer: Curd and sour substances contain acids. These acids react with copper and brass to form poisonous metal salts, which can contaminate the food and cause health hazards. Hence, such substances should not be kept in brass or copper vessels.
2. Which gas is usually liberated when an acid reacts with a metal? Illustrate with an example. How will you test for the presence of this gas?
Answer: When an acid reacts with a metal, hydrogen gas is usually liberated.
Example: Zn+2HCl→ZnCl2+H2↑
Test: Bring a burning matchstick near the gas. Hydrogen burns with a ‘pop’ sound, confirming its presence.
3. Metal compound A reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce effervescence. The gas evolved extinguishes a burning candle. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction if one of the compounds formed is calcium chloride.
Answer: The gas that extinguishes a burning candle is carbon dioxide. Therefore, metal compound A is calcium carbonate.
Balanced Chemical Equation: CaCO3+2HCl→CaCl2+H2O+CO2↑
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Questions: Page – 25
1. Why do HCl, HNO3, etc.. show acidic characters in aqueous solutions while solutions of compounds like alcohol and glucose do not show acidic character?
Answer: HCl, HNO₃, etc. produce hydrogen ions (H⁺) or hydronium ions (H₃O⁺) in aqueous solutions, which are responsible for acidic character. Alcohol and glucose do not ionize in water to produce H⁺ ions; therefore, they do not show acidic character.
2. Why does an aqueous solution of an acid conduct electricity?
Answer: An aqueous solution of an acid conducts electricity because it contains free ions (H₃O⁺ and corresponding anions) which act as charge carriers.
3. Why does dry HCl gas not change the colour of the dry litmus paper?
Answer: Dry HCl gas does not produce hydronium ions in the absence of water. Since acidity is due to the presence of H₃O⁺ ions, dry HCl gas does not change the colour of dry litmus paper.
4. While diluting an acid, why is it recommended that the acid should be added to water and not water to the acid?
Answer: Dilution of acids is highly exothermic. If water is added to acid, the heat produced may cause the acid to splash, leading to burns. Adding acid slowly to water allows the heat to be absorbed safely, preventing accidents.
5. How is the concentration of hydronium ions (H3O+) affected when a solution of an acid is diluted?
Answer: When an acid solution is diluted, the concentration of hydronium ions (H₃O⁺) decreases, making the solution less acidic.
6. How is the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH–) affected when excess base is dissolved in a solution of sodium hydroxide?
Answer: When excess base is dissolved in a sodium hydroxide solution, the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH⁻) increases, making the solution more basic.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Questions: Page – 28
1. You have two solutions, A and B. The pH of solution A is 6 and pH of solution B is 8. Which solution has more hydrogen ion concentration? Which of this is acidic and which one is basic?
Answer: Solution A (pH 6) has a higher hydrogen ion (H⁺) concentration than solution B (pH 8). Since pH less than 7 indicates acidity, solution A is acidic, whereas solution B is basic.
2. What effect does the concentration of H+(aq) ions have on the nature of the solution?
Answer: The nature of a solution depends on the concentration of H⁺(aq) ions.
- Higher concentration of H⁺ ions → more acidic solution
- Lower concentration of H⁺ ions → less acidic or basic solution
3. Do basic solutions also have H+(aq) ions? If yes, then why are these basic?
Answer: Yes, basic solutions also contain H⁺(aq) ions. However, they are basic because the concentration of OH⁻ ions is much higher than that of H⁺ ions in the solution.
4. Under what soil condition do you think a farmer would treat the soil of his fields with quick lime (calcium oxide) or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) or chalk (calcium carbonate)?
Answer: A farmer would treat the soil with quick lime (CaO), slaked lime [Ca(OH)₂], or chalk (CaCO₃) when the soil is too acidic. These substances are basic in nature and help neutralize the acidity of the soil, thereby improving soil fertility.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Questions: Page – 33
1. What is the common name of the compound Ca(ClO)2?
Answer: The common name of Ca(ClO)₂ is bleaching powder.
2. Name the substance which on treatment with chlorine yields bleaching powder.
Answer: Dry slaked lime [Ca(OH)₂] on treatment with chlorine yields bleaching powder.
3. Name the sodium compound which is used for softening hard water.
Answer: Sodium carbonate (washing soda) is used for softening hard water.
4. What will happen if a solution of sodium hydrocarbonate is heated? Give the equation of the reaction involved.
Answer: On heating sodium hydrogencarbonate solution, it decomposes to form sodium carbonate, water, and carbon dioxide.
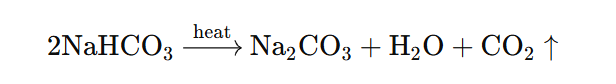
5. Write an equation to show the reaction between Plaster of Paris and water.
Answer: Plaster of Paris) → (Gypsum