
Chemical reaction and equation class 10 notes are one of the most important study resources for every Class 10 student who wants to understand science easily and score high marks in exams. This chapter is the first step into real chemistry, where you learn how substances change, how reactions happen, and how to write and balance chemical equations correctly. Many students find this chapter confusing at first, but with the right explanation, it becomes simple, interesting, and even fun to learn.
That is why in this blog, you will find NCERT | NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reaction and Equation Class 10 Notes explained in a clear, simple, and exam-focused way. These notes are perfect for quick revision before tests, doubt-clearing study sessions, and last-minute board exam preparation. With easy language, real-life examples, and important exam points, this guide will help you build strong concepts and boost your confidence in chemistry.
- Chemical Reaction and Equation: (Chemical Reaction and Equation Class 10 Notes)
- Chemical Equations: (Chemical Reaction and Equation Class 10 Notes)
- Balanced Chemical Equations – Step by Step (Short & with Tables:
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Questions: Page -6
- Types of Chemical Reactions:
- Difference between Combination Reaction and Decomposition Reaction:
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Questions: Page -10
- Recall Activity 1.1: Page -13
- Corrosion and Rancidity: (Chemical Reaction and Equation Class 10 Notes)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Questions: Page -13
- Need to Know: (Chemical Reaction and Equation Class 10 Notes)
- EXERCISES: (Page 14-16) (Chemical Reaction and Equation Class 10 Notes)
NCERT | Chemical Reaction and Equation Class 10 Notes – Simple Explanation with Examples (FREE PDF)
Chemical Reaction and Equation: (Chemical Reaction and Equation Class 10 Notes)
What is a chemical reaction?
Answer: A chemical reaction is a process in which one or more substances change into new substances with different properties.
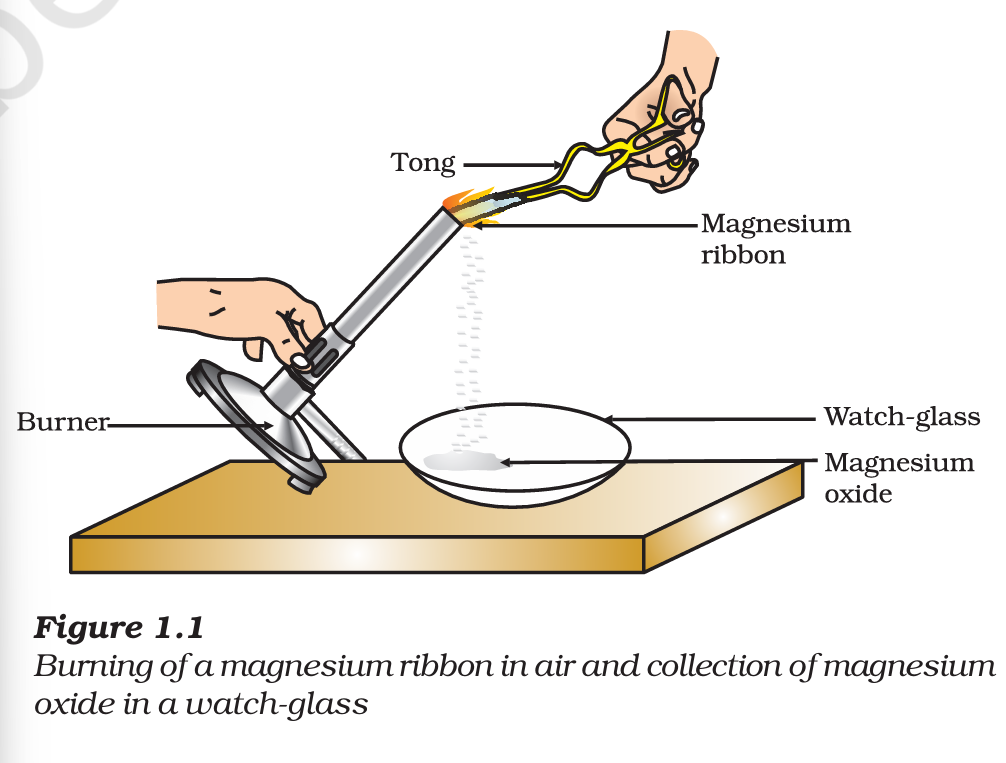
Example: When magnesium burns in air and it reacts with oxygen in the presence of moisture, it forms magnesium oxide.
Magnesium + Oxygen -> Magnesium Oxide
This is a chemical reaction because a new substance (magnesium oxide) is formed.
Chemical Equations: (Chemical Reaction and Equation Class 10 Notes)
The previous reaction can be described as – when a magnesium ribbon is burnt in oxygen, it gets converted to magnesium oxide. This description of a chemical reaction in a sentence form is quite long. It can be written in a shorter form. The simplest way to do this is to write it in the form of a word equation.
The word-equation for the above reaction would be
Magnesium + Oxygen -> Magnesium oxide (Product).
Mg + O₂ -> MgO (Where magnesium and oxygen are reactants, and magnesium oxide is the product.)
Download Chemical Reaction and Equation Class 10 Notes Free
Balanced Chemical Equations – Step by Step (Short & with Tables:
A balanced chemical equation is an equation in which the number of atoms of each element is equal on both sides of the equation, following the Law of Conservation of Mass.
Count and compare the number of atoms of each element on the LHS and RHS of the arrow. Is the number of atoms of each element the same on both the sides? If yes, then the equation is balanced. If not, then the equation is unbalanced because the mass is not the same on both sides of the equation. Such a chemical equation is a skeletal chemical equation for a reaction.
General Steps to Balance a Chemical Equation (Short):
- Write the unbalanced equation.
- Count the number of atoms of each element on both sides.
- Balance one element at a time using coefficients (not subscripts).
- First balance metals -> non-metals -> hydrogen -> oxygen.
- Recheck all atoms on both sides.
- Write the final balanced equation.
Example 1: Hydrogen + Oxygen -> Water:
Unbalanced Equation: H₂ + O₂ -> H₂O
Step 1: Atom Count Table
| Element | Left Side (LHS) | Right Side (RHS) |
|---|---|---|
| H | 2 | 2 |
| O | 2 | 1 |
Remarks – Oxygen is not balanced.
Step 2: Balance Oxygen and Hydrogen
2 H₂ + O₂ -> 2 H₂O
| Element | Left Side (LHS) | Right Side (RHS) |
|---|---|---|
| H | 4 | 4 |
| O | 2 | 2 |
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Questions: Page -6
1. Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air?
Answer: Magnesium gets covered with a layer of magnesium oxide when kept in air for a long time. This layer hinders the burning of magnesium. Hence, it is to be cleaned before burning.
2. Write the balanced equation for the following chemical reactions.
- Hydrogen + Chlorine -> Hydrogen chloride
- Barium chloride + Aluminium sulphate -> Barium sulphate + Aluminium chloride
- Sodium + Water -> Sodium hydroxide + Hydrogen
Answer:
(i) H2 + Cl2 -> 2HCl
(ii) 3 BaCl2 + Al2(SO4)3 -> BaSO4 + 2 AlCl3
(iii) 2Na + 2H2O -> 2NaOH + H2↑
3. Write a balanced chemical equation with state symbols for the following reactions.
- Solutions of barium chloride and sodium sulphate in water react to give insoluble barium sulphate and the solution of sodium chloride.
- Sodium hydroxide solution (in water) reacts with hydrochloric acid solution (in water) to produce sodium chloride solution and water.
Answer:
(i) BaCl2 (aq) + Na2SO4 (aq) -> BaSO4(s) + 2NaCl (aq)
(ii) NaOH (aq) + HCl(aq) -> NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
Download Chemical Reaction and Equation Class 10 Notes Free
Types of Chemical Reactions:
Chemical reactions can be classified into different types based on how reactants change into products. Some major types include:
- Combination Reaction
- Decomposition Reaction
- Displacement Reaction
- Double Displacement Reaction
- Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reaction
- Precipitation Reaction
- Neutralisation Reaction
1. Combination Reaction (Chemical Reaction and Equation Class 10 Notes)
A combination reaction is a chemical reaction in which two or more substances combine to form a single product.
General Form:
A + B -> AB
This means two reactants → One product
Example: Formation of Calcium Oxide (Quicklime)
CaO is formed when calcium reacts with oxygen.
Equation:
2 Ca(s) + O₂(g) -> 2 CaO(s)
Note – Combination reactions are usually exothermic (release heat).
2. Decomposition Reaction (Chemical Reaction and Equation Class 10 Notes)
A decomposition reaction is a chemical reaction in which a single compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances.
General Form:
AB -> A + B
This means:
One reactant -> Two or more products
Types of Decomposition Reactions:
Decomposition can occur due to:
- Heat -> Thermal decomposition
- Electricity -> Electrolytic decomposition
- Light -> Photochemical decomposition
Example 1: Thermal Decomposition of Calcium Carbonate
Equation : CaCO₃(s) -> CaO(s) + CO₂(g)
Here, heat breaks calcium carbonate into calcium oxide + carbon dioxide
Example 2: Electrolysis of Water (Electrolytic Decomposition)
Equation : 2 H₂O(l) -> 2 H₂(g) + O₂(g)
Here, electricity breaks water into hydrogen and oxygen gases.
Difference between Combination Reaction and Decomposition Reaction:
| Feature | Combination Reaction | Decomposition Reaction |
|---|---|---|
| Reactants | Two or more | One compound |
| Products | One product | Two or more products |
| Nature | Usually exothermic | Usually endothermic |
| General form | A + B -> AB | AB -> A + B |
| Example | 2Mg + O₂ -> 2MgO | CaCO₃ -> CaO + CO₂ |
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Questions: Page -10
1. A solution of a substance ‘X’ is used for whitewashing.
- Name the substance ‘X’ and write its formula.
- Write the reaction of the substance ‘X’ named in (i) above with water.
Answer:
(i) The substance ‘X’ is Calcium Oxide, commonly called Quicklime.
Formula: CaO
(ii) CaO(s) + H₂O(l) -> Ca(OH)₂(aq)
2. Why is the amount of gas collected in one of the test tubes in Activity 1.7 double of the amount collected in the other? Name this gas.
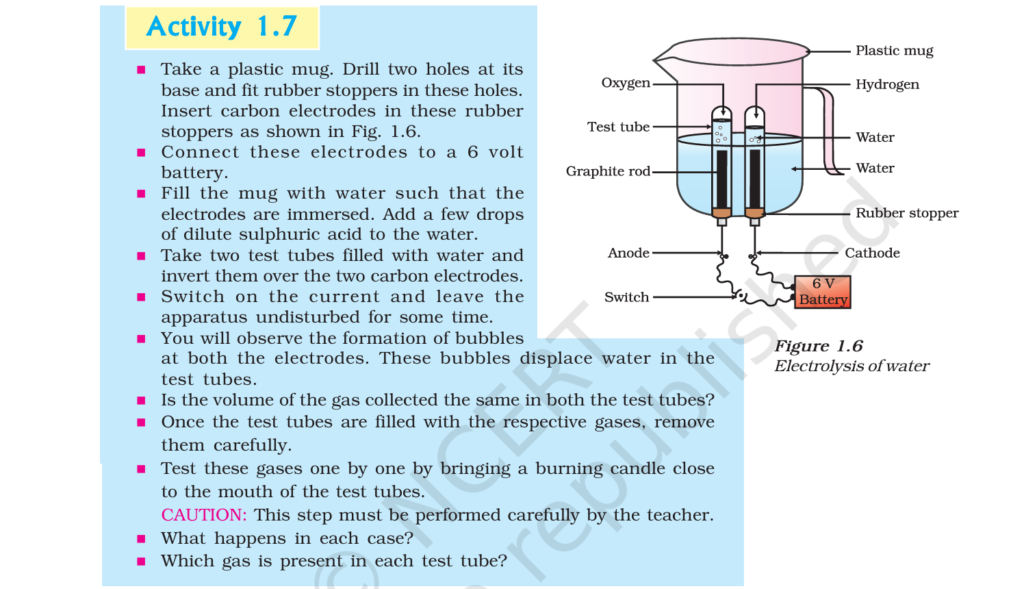
Answer: In Activity 1.7, water is electrolysed to give H₂ gas at one electrode and O2 gas at the other electrode.
2H₂O(l) -> 2H₂(g) + O₂(g)
Thus, two molecules of water on electrolysis give two molecules of hydrogen gas and one molecule of oxygen gas or in other words, the amount of hydrogen gas collected would be double than that of oxygen gas.
3. Displacement Reaction (Chemical Reaction and Equation Class 10 Notes)
A displacement reaction is a reaction in which a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its compound.
General Form: A + BC -> AC + B (Here, A is more reactive than B)
Example : Iron displaces copper from copper sulphate solution
Fe(s) + CuSO₄(aq) -> FeSO₄(aq) + Cu(s)
Note: Iron is more reactive than copper.
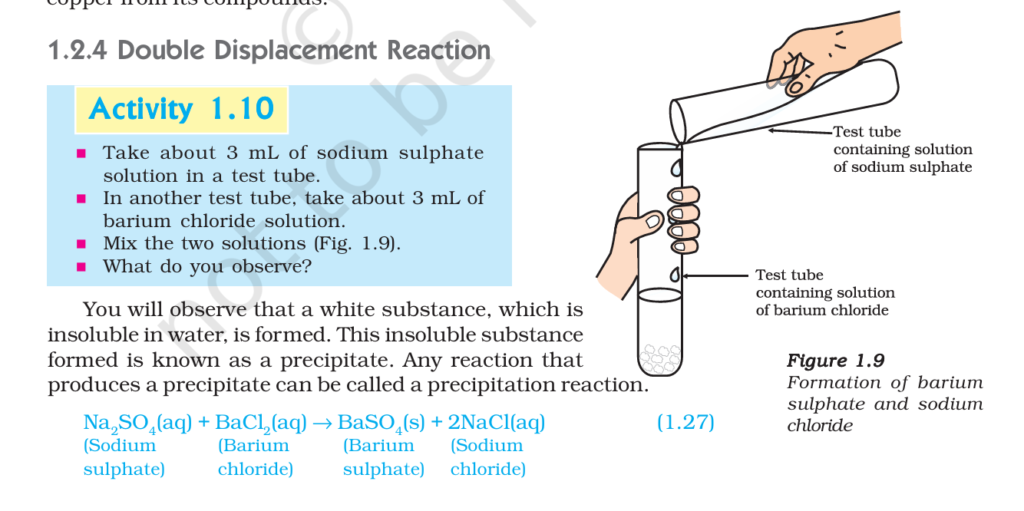
4. Double Displacement Reaction (Chemical Reaction and Equation Class 10 Notes)
A double displacement reaction is a reaction in which the ions of two compounds exchange their partners to form new compounds.
General Form: AB + CD -> AD + CB
Example : Reaction between sodium sulphate and barium chloride:
Na₂SO₄(aq) + BaCl₂(aq) -> BaSO₄(s) + 2 NaCl(aq)
Here, Na⁺ exchanges with Ba²⁺ -> forming new substances.
This reaction also forms a precipitate (BaSO₄), so it is also called a precipitation reaction.
5. Oxidation (NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1)
Oxidation is a process in which:
- A substance gains oxygen, or
- Loses hydrogen, or
- Loses electrons (e⁻)
Example : Magnesium burns in oxygen to form magnesium oxide:
2 Mg(s) + O₂(g) -> 2 MgO(s) (Magnesium gains oxygen, so it is oxidised)
5. Reduction (NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1)
Reduction is a process in which:
- A substance loses oxygen, or
- Gains hydrogen, or
- Gains electrons (e⁻)
Example : Copper oxide is reduced to copper by hydrogen:
CuO(s) + H₂(g) -> Cu(s) + H₂O(l)
Copper oxide loses oxygen, so it is reduced. Hydrogen gains oxygen, so hydrogen is oxidised.
Recall Activity 1.1: Page -13
Where a magnesium ribbon burns with a dazzling flame in air (oxygen) and changes into a white substance, magnesium oxide. Is magnesium being oxidised or reduced in this reaction?
Answer: When magnesium ribbon burns in air, it reacts with oxygen to form magnesium oxide:
2Mg(s) + O₂(g) → 2MgO(s)
In this reaction, magnesium gains oxygen. Since the addition of oxygen is called oxidation, magnesium is being oxidised.
Corrosion and Rancidity: (Chemical Reaction and Equation Class 10 Notes)
Corrosion
Corrosion is the gradual destruction of metals when they react with moisture, oxygen, acids, or other chemicals present in the environment.
When a metal is exposed to air and moisture for a long time, it forms a layer of an unwanted compound (like oxides or carbonates) on its surface. This weakens the metal.
Example: Rusting of iron
4Fe + 3O₂ + 2H₂O -> 2Fe₂O₃·xH₂O (Rust)
Iron reacts with oxygen and moisture to form a brown, flaky substance called rust.
Rancidity
Rancidity is the process in which oily and fatty foods get spoiled due to oxidation, resulting in a bad smell and taste.
When fats and oils come in contact with air for a long time, they undergo oxidation. This causes the food to develop an unpleasant smell and become unfit for eating.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Questions: Page -13
1. Why does the colour of copper sulphate solution change when an iron nail is dipped in it?
Answer: When an iron nail is dipped in copper sulphate solution, the displacement reaction takes place. The colour of copper sulphate solution fades due to the formation of light green solution of iron sulphate.
This happens because iron is more reactive than copper. So, iron displaces copper from copper sulphate solution and forms iron sulphate (FeSO₄), which is green in colour.
Fe(s) + CuSO₄(aq) -> FeSO₄(aq) + Cu(s)
Thus, the colour changes from blue to green due to the formation of iron sulphate.
2. Give an example of a double displacement reaction other than the one given in Activity 1.10.
Answer: A common example of a double displacement reaction is the reaction between silver nitrate and sodium chloride solutions.
Example: When silver nitrate (AgNO₃) solution is mixed with sodium chloride (NaCl) solution, a white precipitate of silver chloride (AgCl) is formed. This happens because the ions exchange their partners.
AgNO₃(aq) + NaCl(aq) -> AgCl(s) ↓ + NaNO₃(aq)
This reaction is a double displacement reaction because the Ag⁺ ion exchanges with the Na⁺ ion, forming a new insoluble precipitate (AgCl).
3. Identify the substances that are oxidised and the substances that are reduced in the following reactions.
- 4Na(s) + O₂(g) -> 2Na₂O(s)
- CuO(s) + H₂(g) -> Cu(s) + H₂O(l)
Answer:
- Substances oxidised: Sodium (Na), Substance reduced: Oxygen (O₂)
- Substances oxidised: Hydrogen (H₂), Substance reduced: Copper(II) oxide (CuO)
Need to Know: (Chemical Reaction and Equation Class 10 Notes)

Revise these points before your exam.
Download Chemical Reaction and Equation Class 10 Notes – Homework Suggestions Free
EXERCISES: (Page 14-16) (Chemical Reaction and Equation Class 10 Notes)
1. Which of the statements about the reaction below are incorrect?
2PbO(s) + C(s) -> 2Pb(s) + CO₂(g)
- Lead is getting reduced.
- Carbon dioxide is getting oxidised.
- Carbon is getting oxidised.
- Lead oxide is getting reduced.
- (a) and (b)
- (a) and (c)
- (a), (b) and (c)
- all
Answer: (i) (a) and (b)
Explanation:
- Lead is getting reduced.❌ – Reduction actually occurs to lead oxide (PbO), not to lead metal directly.
- Carbon dioxide is getting oxidised. ❌ – Carbon dioxide is already a fully oxidised compound, so it cannot be oxidised further.
2. Fe₂O₃ + 2AI -> Al₂O₃ + 2Fe
The above reaction is an example of a
- combination reaction.
- double displacement reaction.
- decomposition reaction.
- displacement reaction.
Answer: (d) displacement reaction.
Explanation: Fe₂O₃ + 2Al -> Al₂O₃ + 2Fe
In this reaction, aluminium, being more reactive than iron, displaces iron from iron(III) oxide to form aluminium oxide and free iron.
Since one element (Al) displaces another element (Fe) from its compound, this reaction is a displacement reaction. This reaction is also known as the thermite reaction.
3. What happens when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to iron fillings? Tick the correct answer.
- Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced.
- Chlorine gas and iron hydroxide are produced.
- No reaction takes place.
- Iron salt and water are produced.
Answer: (a) Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced.
Explanation: When dilute hydrochloric acid is added to iron filings, iron reacts with the acid to form iron chloride and hydrogen gas.
Chemical Equation: Fe(s) + 2HCl(aq) -> FeCl₂(aq) + H₂(g)
4. What is a balanced chemical equation? Why should chemical equations be balanced?
Answer: A balanced chemical equation is a chemical equation in which the number of atoms of each element is equal on both the reactant side and the product side of the equation.
Chemical equations should be balanced because they follow the Law of Conservation of Mass, which states that mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
5. Translate the following statements into chemical equations and then balance them.
- Hydrogen gas combines with nitrogen to form ammonia.
- Hydrogen sulphide gas burns in air to give water and sulpur dioxide.
- Barium chloride reacts with aluminium sulphate to give aluminium chloride and a precipitate of barium sulphate.
- Potassium metal reacts with water to give potassium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
Answer: Chemical Equations
- N₂ + H₂ -> NH₃
- H₂S + O₂ -> H₂O + SO₂
- BaCl₂ + Al₂(SO₄)₃ -> AlCl₃ + BaSO₄
- K + H₂O -> KOH + H₂
Balanced Chemical Equations:
- N₂ + 3H₂ -> 2NH₃
- 2H₂S + 3O₂ -> 2H₂O + 2SO₂
- 3BaCl₂ + Al₂(SO₄)₃ -> 2AlCl₃ + 3BaSO₄
- 2K + 2H₂O -> 2KOH + H₂
Chemical Reaction and Equation Class 10 Notes
6. Balance the following chemical equations.
- HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 -> Ca(NO3)2 + H20
- NaOH + H2SO4 -> Na2SO4 + H20
- NaCl + AgNO3 -> AgCl + NaNO3
- BaCl2 + H2SO4 -> BaSO4 + HCl
Answer: Balanced Chemical Equations:
- 2HNO₃ + Ca(OH)₂ -> Ca(NO₃)₂ + 2H₂O
- 2NaOH + H₂SO₄ -> Na₂SO₄ + 2H₂O
- NaCl + AgNO₃ -> AgCl + NaNO₃
- BaCl₂ + H₂SO₄ -> BaSO₄ + 2HCl
7. Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions.
- Calcium hydroxide + Carbon dioxide –> Calcium carbonate + Water
- Zinc + Silver nitrate –> Zinc nitrate + Silver
- Aluminium + Copper chloride –> Aluminium chloride + Copper
- Barium chloride + Potassium sulphate –> Barium sulphate + Potassium chloride
Answer: Balanced chemical equations
- Ca(OH)₂ + CO₂ -> CaCO₃ + H₂O
- Zn + 2AgNO₃ -> Zn(NO₃)₂ + 2Ag
- 2Al + 3CuCl₂ -> 2AlCl₃ + 3Cu
- BaCl₂ + K₂SO₄ -> BaSO₄ + 2KCl
8. Write the balanced chemical equation for the following and identify the type of reaction in each case.
- Potassium bromide(aq) + Barium iodide(aq) → Potassium iodide(aq) + Barium bromide(s)
- Zinc carbonate(s) → Zinc oxide(s) + Carbon dioxide(g)
- Hydrogen(g) + Chlorine(g) → Hydrogen chloride(g)
- Magnesium(s) + Hydrochloric acid(aq) → Magnesium chloride(aq) + Hydrogen(g)
Answer: Balanced Chemical Equations with Type of Reaction
- 2KBr(aq) + BaI₂(aq) -> 2KI(aq) + BaBr₂(s) —- Double displacement reaction
- ZnCO₃(s) -> ZnO(s) + CO₂(g) —- Decomposition reaction
- H₂(g) + Cl₂(g) -> 2HCl(g) —- Combination reaction
- Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) -> MgCl₂(aq) + H₂(g) —- Displacement reaction
9. What does one mean by exothermic and endothermic reactions? Give examples.
Answer: An exothermic reaction is a chemical reaction in which heat energy is released to the surroundings.
Example: C + O₂ -> CO₂ + Heat
An endothermic reaction is a chemical reaction in which heat energy is absorbed from the surroundings.
Example: CaCO₃ -> CaO + CO₂ (Heat is absorbed)
10. Why is respiration considered an exothermic reaction? Explain.
Answer: Respiration is considered an exothermic reaction because energy is released during the breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen. This released energy is used by the body for various life processes such as movement, growth, and repair.
Chemical Equation: C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ -> 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Energy
Chemical Reaction and Equation Class 10 Notes
11. Why are decomposition reactions called the opposite of combination reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Answer: Decomposition reactions are called the opposite of combination reactions because:
In a combination reaction, two or more substances combine to form a single product. In the other hand In a decomposition reaction, a single compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances.
Example of combination reaction: CaO + H₂O -> Ca(OH)₂
Example of decomposition reaction: Ca(OH)₂ -> CaO + H₂O
12. Write one equation each for decomposition reactions where energy is supplied in the form of heat, light or electricity.
Answer: I am giving the examples below
Decomposition by heat (Thermal decomposition): CaCO₃(s) -> CaO(s) + CO₂(g)
Decomposition by light (Photochemical decomposition): 2AgCl(s) -> 2Ag(s) + Cl₂(g)
Decomposition by electricity (Electrolytic decomposition): 2H₂O(l) -> 2H₂(g) + O₂(g)
13. What is the difference between displacement and double displacement reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Answer:
| Displacement reaction | Double displacement reaction |
|---|---|
| A displacement reaction is a reaction in which a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its compound. | A double displacement reaction is a reaction in which ions of two compounds exchange their partners to form new compounds. |
| Example – Zn(s) + CuSO₄(aq) -> ZnSO₄(aq) + Cu(s) | Example – Na₂SO₄(aq) + BaCl₂(aq) -> BaSO₄(s) + 2NaCl(aq) |
14. In the refining of silver, the recovery of silver from silver nitrate solution involved displacement by copper metal. Write down the reaction involved.
Answer: When copper metal is added to silver nitrate solution, copper displaces silver from the solution.
Chemical Equation: Cu(s) + 2AgNO₃(aq) -> Cu(NO₃)₂(aq) + 2Ag(s)
15. What do you mean by a precipitation reaction? Explain by giving examples.
Answer: A precipitation reaction is a chemical reaction in which two aqueous solutions react to form an insoluble solid, called a precipitate.
The precipitate separates out from the solution during the reaction.
Examples:
- BaCl₂(aq) + Na₂SO₄(aq) -> BaSO₄(s) + 2NaCl(aq) — Barium sulphate is the white precipitate
- AgNO₃(aq) + NaCl(aq) -> AgCl(s) + NaNO₃(aq) — Silver chloride is the white precipitate
Chemical Reaction and Equation Class 10 Notes
16. Explain the following in terms of gain or loss of oxygen with two examples each.
- Oxidation
- Reduction
Answer:
(a) Oxidation: Oxidation is a process in which a substance gains oxygen or loses hydrogen.
Examples:
- 2Mg + O₂ -> 2MgO — Magnesium gains oxygen
- Cu + O₂ -> CuO — Copper gains oxygen
(b) Reduction: Reduction is a process in which a substance loses oxygen or gains hydrogen.
Examples:
- CuO + H₂ -> Cu + H₂O — Copper oxide loses oxygen
- Fe₂O₃ + 3CO -> 2Fe + 3CO₂ — Iron oxide loses oxygen
17. A shiny brown coloured element ‘X’ on heating in air becomes black in colour. Name the element ‘X’ and the black coloured compound formed.
Answer: The shiny brown coloured element ‘X’ is Copper (Cu). When copper is heated in air, it reacts with oxygen to form a black coloured compound called Copper(II) oxide (CuO).
Chemical Reaction: 2Cu + O₂ -> 2CuO
18. Why do we apply paint on iron articles?
Answer: Paint is applied on iron articles to prevent rusting. The paint forms a protective layer on iron and prevents contact with air and moisture, which are necessary for rusting.
19. Oil and fat containing food items are flushed with nitrogen. Why?
Answer: Oil and fat containing food items are flushed with nitrogen gas to prevent rancidity.
Nitrogen is an inert gas and does not react with oils and fats, thus preventing their oxidation and increasing the shelf life of food items.
20. Explain the following terms with one example each.
- Corrosion
- Rancidity
Answer: Here is the explanation,
(a) Corrosion: Corrosion is the slow destruction of metals due to their reaction with air, moisture, or chemicals.
Example: Rusting of iron.
(b) Rancidity: Rancidity is the process in which oils and fats get spoiled due to oxidation, resulting in a bad smell and taste.
Example: Spoilage of chips or fried food when kept in open air.
Chemical Reaction and Equation Class 10 Notes

Very clean site, thanks for this post.