In today’s digital world, the CBSE | Computer and its Components | Class 10 | Chapter 1 Solutions play a vital role in shaping how we work, learn, and communicate. From performing complex calculations to managing everyday tasks, computers have become an inseparable part of our lives. Understanding the computer and its components helps us appreciate how this powerful machine operates
Table of Contents
Computer And Its Components Question Answer Class 10 Solutions | CBSE
What is a computer?
Answer: The computer is just a dead collection of plastic, silicon, and metal until you press the ‘Power’ button. One little burst of electricity and it starts a string of events that puts life and power into the machine.
What is the full form of computer?
Answer: Common Operating Machine Purposely Used for Technological and Educational Research (COMPUTER)
Who is known as the father of computer?
Answer: Charles Babbage is known as the father of the computer.
What is data?
Answer: data is a collection of unprocessed facts, figures, and symbols.
What is information?
Answer: Information is a processed form of data. It is organized, meaningful, and useful.
Hardware and Software
In the process of converting data to information, a computer uses hardware and software.
At the simplest level, all computers consist of these two basic components: the hardware and the software.
Hardware
Hardware is any part of the computer that has a physical structure that can be seen and touched, though some may be so tiny that they are invisible to the naked eye.
Types of Hardware Components:
- Input Devices: Input devices are the devices that allow a user to enter data and instructions into a computer. Example- keyboard, mouse, microphone, scanner, trackball, joystick, graphics tablet and digital camera.
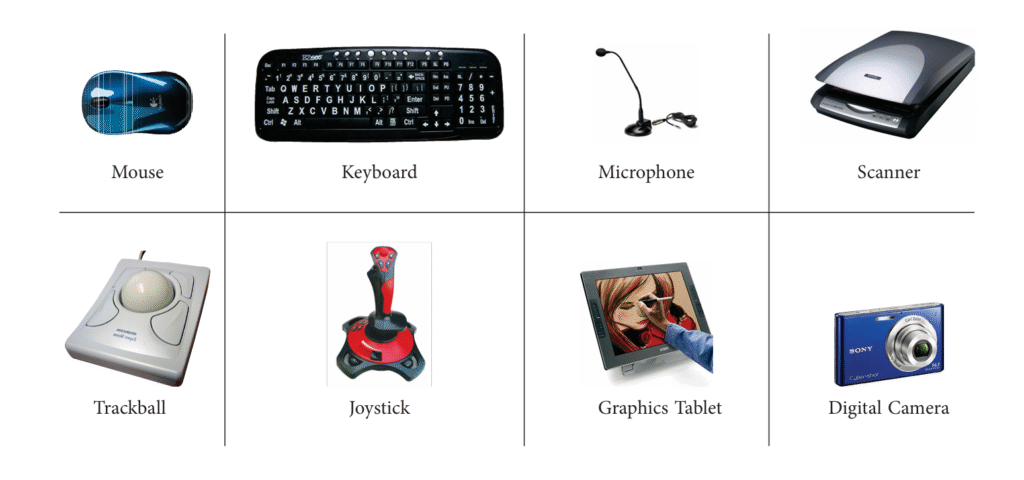

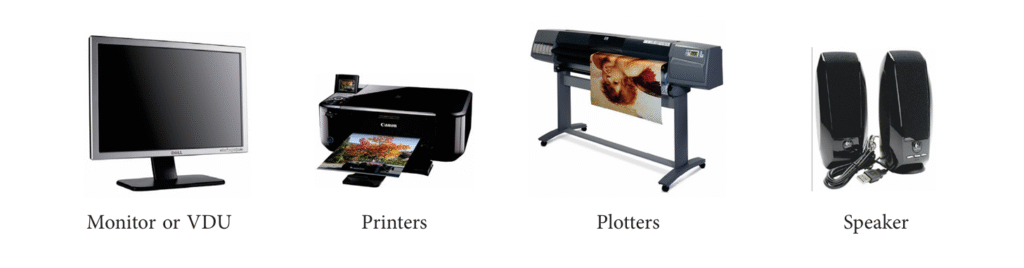
- Output Devices: Output devices are used to display the result or information to the user through monitor or VDUs, LCDs, printers, plotters and speakers.
- Storage Devices: storage devices are the devices which are used to retrieved from and saved to the data and information. Example: hard drives, memory sticks (pen drives), compact discs, DVDs and tape drives.
CPU (Central Processing Unit)
A central processing unit (CPU) is the primary functional component of a computer. The CPU is an assemblage of electronic circuitry that run a computer’s operating system and apps and manages a variety of other computer operations.
A CPU is, essentially, the active brain of the computer. The CPU is the invisible manager inside the computer where data input is transformed into information output. It consists of the arithmetic and logic unit (ALU), which executes most computer operations (arithmetic and logical), and the control unit, which acts as the nerve center that sends control signals to all other units.
Like the human brain, the CPU can multitask. This means it is also the part of the computer that simultaneously regulates the computer’s internal functions, oversees power consumption, allocates computing resources, and interfaces with various apps, programs, and networks.
Memory
There are two categories of memory, primary memory and secondary memory
Primary Memory: Primary Memory is very fast as data and programs must be in the primary memory for execution. Random Access Memory (RAM) and Read Only Memory (ROM) are both
primary memory.
- Random Access Memory (RAM): refers to memory that can be selected and used randomly. The information stored here disappears the very moment the machine is turned off. It is also referred to as volatile memory.
- Read Only Memory (ROM): It is permanently built into the computer at the time of production. The information from this memory can only be read and it is not possible to write fresh information into it.
Units of Memory:

Software
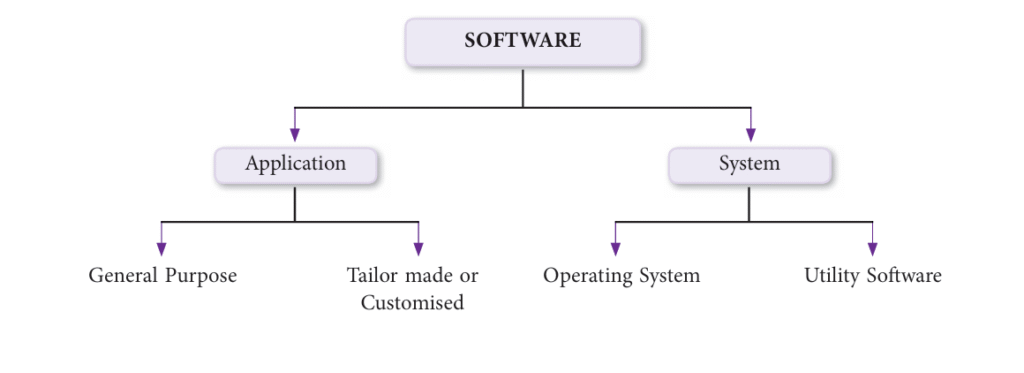
Software is the instruction set that tells the computer how to perform tasks.
Input devices, output devices, a system unit, storage devices, and communication devices are all components of computer hardware.
- Application Software: It includes programs that direct the computer to carry out specific tasks. Often, multiple programs are integrated to create an application.
- System Software: System software includes the programs that enable the computer’s hardware to work with and run the application software. System software is the interface between user and the other programs and the computer’s hardware.
Computers characteristics
- Speed: A computer computes problems much faster than a human being.
- Accuracy: With the high computation speed, computers are able to produce accurate results. If the input is valid, only then correct output will be produced, as computers follows GIGO i.e. Garbage In Garbage Out principle.
- No IQ: It is programmed to carry out tasks and performs exactly as instructed, since it has no intelligence of its own.
- Data Storage: Using different kinds of storage devices, it can store huge quantities of data over long periods of time.
- No Heuristics: As a computer is a dumb machine, thus it never ever learns from its past experiences.
Generations of Computers
Computers have been divided into five generations according to the development of technologies used to fabricate the processors, memories and I/O units.
- I Generation (1945 – 55): These computers were used mainly for scientific calculations. Examples: ENIAC, EDSAC, EDVAC, UNIVAC.
- II Generation (1955 – 65): Smaller than 1st generation computers, but better performance-wise. These computers used transistors instead of vacuum tubes.
- III Generation (1965 – 75): Small Scale Integration and Medium Scale Integration technology were implemented in CPU, I/O processors, etc. Faster processors with magnetic core memories that were later replaced by RAM and ROM.
- IV Generation (1975 – 89): In this generation, microprocessors were introduced where complete processors and large section of main memory could be implemented in a single chip.
- V Generation (1989 to present): Computers use extensive parallel processing, multiple pipelines, multiple processors etc.
Categories of Computers
Computers are classified into many categories depending upon their size, functioning and processing capabilities.
According to how it functions, computers can be classified into three categories.
- Analog Computers: According to the Merriam Webster Dictionary, computers in which continuously variable physical quantities, such as electrical potential, fluid pressure, or mechanical motion, are used to represent (analogously) the quantities in the problem to be solved are called analog computers.
- Digital Computers: These computers deal with data in the form of numbers. They mainly operate by counting and performing arithmetic & logical operations on numeric data. Such computers are ‘many problems’ oriented.
- Hybrid: Digital computers could not deal with very large numbers and so, a computer with characteristics of both analog and digital was created, which was known as Hybrid computer.
According to the size, computers can be classified into the following categories.
- Palmtop: better known as personal digital assistants.
- Laptops and Notebooks: these are the portable computers.
- Personal Computer (PC): These computers is small in size and designed for general use by a single person.
- Desktop: This computer is typically set up in a permanent location and is a PC that is not portable.
- Micro Computers: came into being with the invention of the micro-processor. They are not so expensive. The personal computer is a micro-computer.
- Mini Computers: These computers provide more power than micro computers in terms of speed and storage capacity.
- Mainframe Computers: These can also process data at very high speeds, but less than that of super computers.
- A Supercomputer: This is the fastest type of computer.
Uses of Computers / Applications of Computers
Computers are used in almost all walks of life today. In medicine and health care, in education and business, in the manufacturing and service industries, for science and research; computers are the most important tool used by human beings.
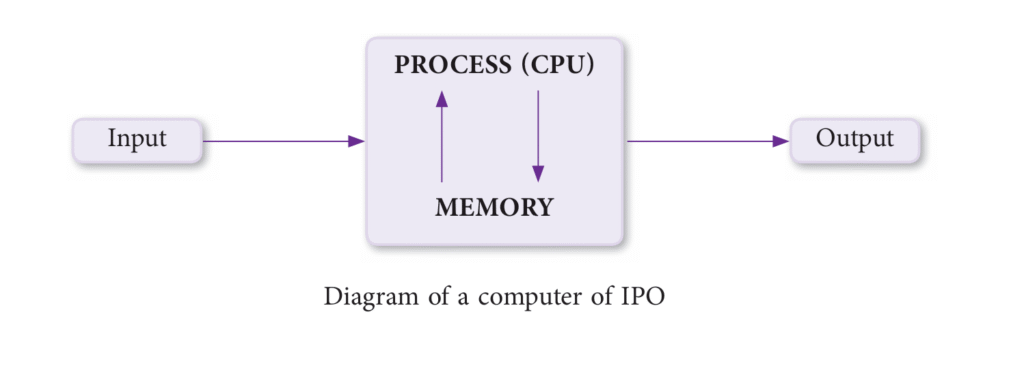
Input -> Process -> Output (IPO) Computer Diagram
Input-Process-Output cycle or IPO refers to the stages that a set of instructions undergo to achieve the desired result. The computer is not a magic box where things get done automatically. The information, through various input devices, is fed into the system to be processed by the CPU. The information is then received as output in the desired format and presented in human readable form.
Computer Ports and Cables
We use computer ports and cables for data transfer from one place to another place. There are several ports example given in your textbook.
- PS/2 Ports
- VGA Monitor Port
- Parallel Port
- Ethernet Port
- S-Video Port
- Video Port
- USB Port
- FireWire IEEE 1394 Port
- Mini Audio Jack
Computer And Its Components Question Answer Class 10 Solutions | Exercise Solve
A. Multiple choice questions
1. The collection of unprocessed facts, figures and symbols is known as ________
- Information
- Software
- Data and Information
- None of the above
Answer: Data and Information
2. ________ is the processed form of data which is organized meaningful and useful.
- Information
- Software
- Data
- None of the above
Answer: Information
3. Hardware is any part of the computer that has a physical structure that can be seen and touched.
- True
- False
- Not sure
- None of the above
Answer: True
4. Components of computer hardware are ________
- Input devices and output devices
- A system unit and storage devices
- Communication devices
- All of the above
Answer: All of the above
5. _________ devices accept data and instructions from the user.
- Output
- Input
- Components of hardware
- Storage
Answer: Input
6. Which disk is made up of a circular thin plastic jacket coated with magnetic material?
- Hard Disk
- Compact Disk
- DVD
- Floppy Disk
Answer: Floppy Disk
7. _________ disks are used to store more than 25 GB of data with a very high speed in less amount of time.
- Digital Versatile
- Compact
- Blue-Ray
- None of the above
Answer: Blue-Ray
8. Random Access Memory and Read Only Memory are examples of ________
- Primary Memory
- Secondary Memory
- Auxiliary Memory
Both Primary and secondary memory
Answer: Primary Memory
9. Which system uses only the digits 0 and 1?
- Bits
- Binary number system
- Secondary number system
- Nibbles
Answer: Binary number system
10. There are two primary types of softwares namely ________ And _________
- General purpose and tailor made
- Operating system and utility software
- Application software and system software
- None of the above
Answer: Application software and system software
11. Gimp, Adobe Photoshop, Corel Draw, Picasa etc. are examples of _________ softwares, spreadsheets
- Word Processors
- Desktop publishing
- Presentation
Answer: Desktop publishing
12. Which generation computers used high level languages such as FORTRAN and COBOL and used transistors instead of vacuum tubes?
- I Generation
- II Generation
- III Generation
- V Generation
Answer:
13. IBM notebooks, Pentium PCs-Pentium 1/2/3/4/Dual core/Quad core, PARAM 10000 are examples of which generation of computers?
- I Generation
- IV Generation
- III Generation
- V Generation
Answer:
14. According to the functioning of computers, they are divided into three categories namely ________, ________ and _________.
- Mainframe, Supercomputer and Mini computer
- Analog, Digital and Hybrid
- Palmtop, PC and Desktop
- Micro-computers, Digital and Hybrid
Answer: Analog, Digital and Hybrid
15. __________ is a cabling technology for transferring data to and from digital devices at high speeds.
- S-video port
- Firewire
- Ethernet Port
- PS/2 port
Answer: Firewire
16. ________ is used to connect the monitor to the computer which offers images at higher resolutons.
- USB port
- Video Graphics Array
- Parallel Port
- None of the above
Answer: Video Graphics Array
B. Answer the following questions
1. Explain the following terms (a) RAM, (b) Nibble, (c) Digital Computers, (d) Ethernet Port
Answer:
- RAM: Stands for Random Access Memory refers to memory that can be selected and used randomly. The information stored here disappears the very moment the machine is turned off. It is also referred to as volatile memory.
- Nibble: A nibble is a small unit of digital data that consists of 4 bits, which is half of a byte. It is often used to represent a single hexadecimal digit (values from 0 to F) in computer systems.
- Digital Computers: hese computers deal with data in the form of numbers. They mainly operate by counting and performing arithmetic & logical operations on numeric data. Such computers are ‘many problems’ oriented.
- Ethernet Port: Ethernet port on most computers are used to connect it to a wired network.
2. Name any two utility softwares.
Answer: Antivirus software and File Compression software
3. Why there is a need of Auxiliary Memory?
Answer: The content on the RAM is erased when electric power is switched off. So, it becomes necessary to store this data for future use, somewhere else. Since, primary storage is expensive too; we need a relatively cheaper form of backup storage which can store vast quantities of information. Thus, secondary Memory devices become an important part of the computer.
4. Differentiate the following
- Hardware vs Software
- RAM vs rOM
- Application Software vs System Software
- Digital vs Analog
Answer:
Hardware vs Software
| Hardware | Software |
|---|---|
| Physical components of a computer that can be seen and touched. | Set of programs and instructions that tell the computer what to do. |
| Without software, hardware cannot function. | Software needs hardware to run. |
| It is tangible. | It is intangible. |
RAM vs ROM
| RAM (Random Access Memeory) | ROM (Read Only Memory) |
|---|---|
| It is volatile memory – data is lost when power is off. | It is non-volatile memory – data remains even when power is off. |
| Used for temporary storage during program execution. | Used for permanent storage of essential instructions. |
| Can be read and written. | Can be read only, not easily written. |
Application Software vs System Software
| Application Software | System Software |
|---|---|
| Designed to perform specific tasks for users. | Designed to control and manage computer hardware. |
| Runs on top of system software. | Acts as a platform for application software. |
| Developed according to user needs. | Developed for system management. |
Digital vs Analog
| Digital computer | Analog Computer |
|---|---|
| Works with discrete (binary) data – 0s and 1s. | Works with continuous data (signals, measurements). |
| Gives exact and accurate results. | Gives approximate results. |
| Faster and more reliable. | Slower and less accurate compared to digital. |
5. Explain the functions of operating systems.
Answer: The operating system (OS) manages the overall functioning of a computer. It controls hardware and software resources, and allows users to interact with the system. It handles file management, memory management, and process control. It also manages input/output operations and ensures the system runs smoothly.
6. Explain in brief all the generations of computer.
Answer:
Computers have been divided into five generations according to the development of technologies used to fabricate the processors, memories and I/O units.
- I Generation (1945 – 55): These computers were used mainly for scientific calculations. Examples: ENIAC, EDSAC, EDVAC, UNIVAC.
- II Generation (1955 – 65): Smaller than 1st generation computers, but better performance-wise. These computers used transistors instead of vacuum tubes.
- III Generation (1965 – 75): Small Scale Integration and Medium Scale Integration technology were implemented in CPU, I/O processors, etc. Faster processors with magnetic core memories that were later replaced by RAM and ROM.
- IV Generation (1975 – 89): In this generation, microprocessors were introduced where complete processors and large section of main memory could be implemented in a single chip.
- V Generation (1989 to present): Computers use extensive parallel processing, multiple pipelines, multiple processors etc.
7. Draw and explain IPO cycle.
Answer:

Input-Process-Output cycle or IPO refers to the stages that a set of instructions undergo to achieve the desired result. The computer is not a magic box where things get done automatically. The information, through various input devices, is fed into the system to be processed by the CPU. The information is then received as output in the desired format and presented in human readable form.
8. Name any 4 application areas of computer.
Answer: Four application areas of computers are:
- Education – For online learning, digital classrooms, and research.
- Banking – For online transactions, ATM services, and record management.
- Healthcare – For patient records, diagnosis, and hospital management.
- Business – For accounting, data analysis, and communication.
9. How the computers are classified according to their processing capabilities.
Answer:
According to the size and processing capabilities, computers can be classified into the following categories.
- Palmtop: better known as personal digital assistants.
- Laptops and Notebooks: these are the portable computers.
- Personal Computer (PC): These computers is small in size and designed for general use by a single person.
- Desktop: This computer is typically set up in a permanent location and is a PC that is not portable.
- Micro Computers: came into being with the invention of the micro-processor. They are not so expensive. The personal computer is a micro-computer.
- Mini Computers: These computers provide more power than micro computers in terms of speed and storage capacity.
- Mainframe Computers: These can also process data at very high speeds, but less than that of super computers.
- A Supercomputer: This is the fastest type of computer.
10. Differentiate between Ethernet Port and USB.
Answer:
| Ethernet Port | USB (Universal Serial Bus) |
|---|---|
| Used to connect a computer to a network or the internet using an Ethernet cable. | Used to connect external devices like keyboards, mice, printers, and storage drives. |
| Transfers data only for networking purposes. | Transfers data and power between devices. |
| Provides faster and more stable internet connectivity. | Provides versatile connectivity for multiple device types. |
B. Lab Session
1. State whether the following statements are true or false
- The input device receives data in machine readable form
- The arithmetic and Logical Unit and the Central Processing Unit are part of the Control Unit.
- The plotter is an input device
- RAM and the ROM storage is effected by the presence of electricity.
Answer:
- False
- False
- False
- False
2. Justify the statement ‘Computers are used only to collect data for science and research as either true or false.
Answer: False ❌. Computers are not used only to collect data for science and research. They are also used in many other fields such as education, business, healthcare, communication, entertainment, banking, and transportation for various purposes like data processing, problem-solving, designing, and automation.
3. Tanya is working on a project in her school. For the same, she wants to store multimedia
information in a portable storage device. Her information is subject to change as per her
needs. Which storage device would you recommend? Why?
Answer: I will recommend her a Pen Drive (USB Flash Drive). Because A pen drive is a portable storage device that can easily store multimedia information such as text, images, audio, and video files. It allows easy editing, deletion, and updating of data as per Tanya’s needs. Moreover, it is small, lightweight, rewritable, and compatible with most computers, making it ideal for school projects.
4. Prem Das is an editor and is currently working in a popular News House group. His job
includes writing stories and articles for his newspaper. For writing his documents, he uses
WordPad and Notepad, but is facing problems with the formatting of the document. He
is also not able to check the grammatical errors. Which type of software should he be
using and why?
Answer: Prem Das should use a word processing software because it provides advanced formatting tools, spell check, and grammar check features that make writing and editing easier and more professional.
5. Mr. Shivank works in a multinational company. He often has to travel in and out of the
country in order to complete his tasks. He wants to buy a computer that is portable
and can be easily carried overseas. Which kind of computer should he buy to store his
important information and data?
Answer: Mr. Shivank who travels frequently and needs to carry a computer abroad, I would recommend buying a laptop for store his important information and data, because these types of computers are portable and include a battery that provides electrical backup for a period of time.
6. Where do you store the set of instructions that gets the computer ready to receive
instructions? Discuss the different tasks performed by the OS.
Answer: The set of instructions that gets the computer ready to receive instructions from the user is stored in the Operating System (OS).
Different tasks perfomed by OS
- File Management: The OS manages files on the storage devices by create, read, update and delete.
- Memory Management: It allocates and deallocates memory to different programs running on the computer.
- User interface: The OS provides an interface (like GUI or Command Line) that allows users to interact with the computer easily.
7. ‘Without prior knowledge, a user cannot interact with the computer’. Do you agree with
this statement? Justify your answer.
Answer: Yes, I agree with this statement. A computer works only when proper instructions are given to it. Without prior knowledge, a user cannot give correct commands or understand how to use the hardware and software.
