
Welcome to the world of Introduction to java.
This is the first article in java series, where we discuss and introduce the basic concept of java that a beginner need to know befor proceeding with the language.
In this article we (ThinkSphereEdu) will focus to build a solid understanding of Java’s core principals and properties.
So lets start the java tutorial and explore the basics that can make us strong in java programming.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Java: A Complete Beginner’s Ultimate Guide to Programming in Java 2025-26
What is Java
In today’s technology, Java is the most preferred language by software developers. It is a class-based, object-oriented programming language. It is also called a cross-platform programming language. This capability is one of its core features and is often summarized by the phrase “Write once, run anywhere” (WORA), which means that compiled Java code can run on all platforms that support Java without the need for recompilation.
History of Java
Java was developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems inc. in 1995 and later acquired by Oracle Corporation.
The language was initially called Oak after an oak tree that stood outside Gosling’s office. Later the project went by the name Green and was finally renamed Java, from Java coffee, a type of coffee from Indonesia.
Download Java

To download Java(JDK) in your laptop visit official website: Click Here
Download Java for Windows:
To download java for your windows Click Here.
Download Java for MacOS:
To download java for your MacOS Click Here.
Download Java for Linux:
To download java for your Linux machine Click Here.
Features of Java (Introduction to Java)
As a programming language, the primary objective of Java is security. And Java is one of the most secure programming language in today’s language market.
In addition to this, Java is one of the most popular programming languages due to a few other qualities.
Some of the most important features of Java are explained below:
- Simplicity: The syntax of Java is simple, clean, and easy to understand. As the syntax of Java is based on C++, it can be easier to understand if you have prior knowledge of C++. Java has already removed many complicated features that are available in C++, like pointers, operator overloading, etc. Also in Java, there is no need to remove unreferenced objects owing to the presence of an automatic garbage collector, adding to the simplicity factor.
- Object-Oriented Programming Language: Java is an object-oriented programming language. We organise our software as a combination of different types of objects that encompass both data and behaviour. This methos helps to make a software simple and easy to maintain.
- Platform Independent: Languages like C, C++ is platform dependent. But Java is a platform independent language. It means ava code can be executed on multiple platforms, for example, Windows, Linux, Sun Solaris, Mac/OS, etc.
- Security: This feature makes Java the most reliable language in today’s generation. Because of this feature, Java is used to develop virus-free systems.
- Robust: Java is a robust programming language. The following factors are responsible for this specific characteristic. Error handling, resilience, stability, adaptability, and user experience.
- Portable: It facilitates us to carry the Java bytecode to any platform without requiring any implementation.
Java Terminologies (Introduction to Java)
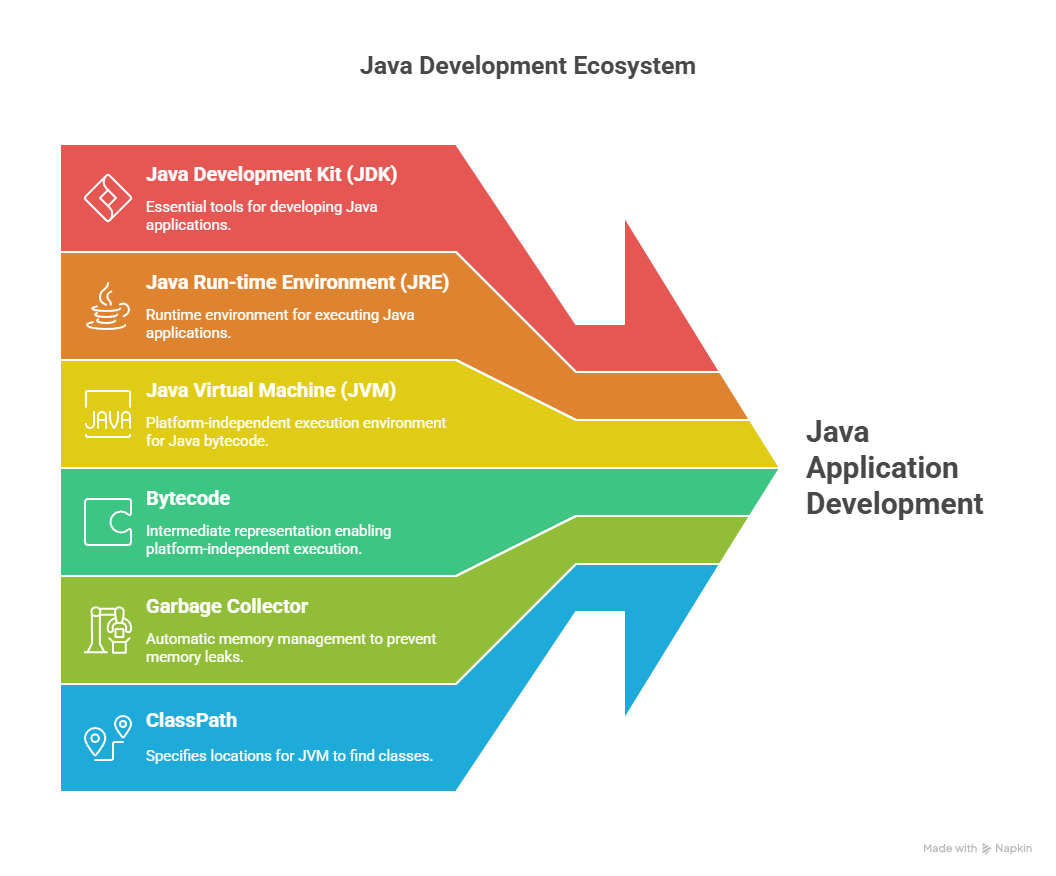
For beginners, familiarity with these terms is fundamental for Java developers to navigate the development and execution lifecycle of Java applications, ensuring efficient coding, portability, and effective memory management.
- Java Development Kit (JDK): JDK stands for Java Development Kit. This kit provides the tools needed for Java development. The Java Development Kit (JDK) is a distribution of Java technology by Oracle Corporation. It implements the Java Language Specification (JLS) and the Java Virtual Machine Specification (JVMS) and provides the Standard Edition (SE) of the Java Application Programming Interface (API)
- Java Run-time Environment (JRE): This is software that Java programs require to run correctly. It provides the environment needed to run the program. It includes the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), a collection of Java standard libraries and core classes, and other supporting files needed for execution.
- Java Virtual Machine (JVM): It is an integral part of both the JDK and JRE. It is a virtualized execution environment that allows Java bytecode to be executed on different platforms without modification. The JRE is for end-users who need to execute Java programs but do not need to develop them.
- Bytecode: This is the intermediate representation of a Java program generated by the Java compiler. The compiler produces bytecode. This bytecode is platform independent. It means, once the bytecode is generated, then we can run this bytecode into another machine and directly get output. No need to compile again. It provides Write Once, Run Anywhere capability.
- Garbage Collector: Garbage collection is a process of programming language that is used for automatic memory management. There is an inbuilt garbage collector available in Java, which automatically collects and destroys the objects that are no longer referenced or needed by the program.
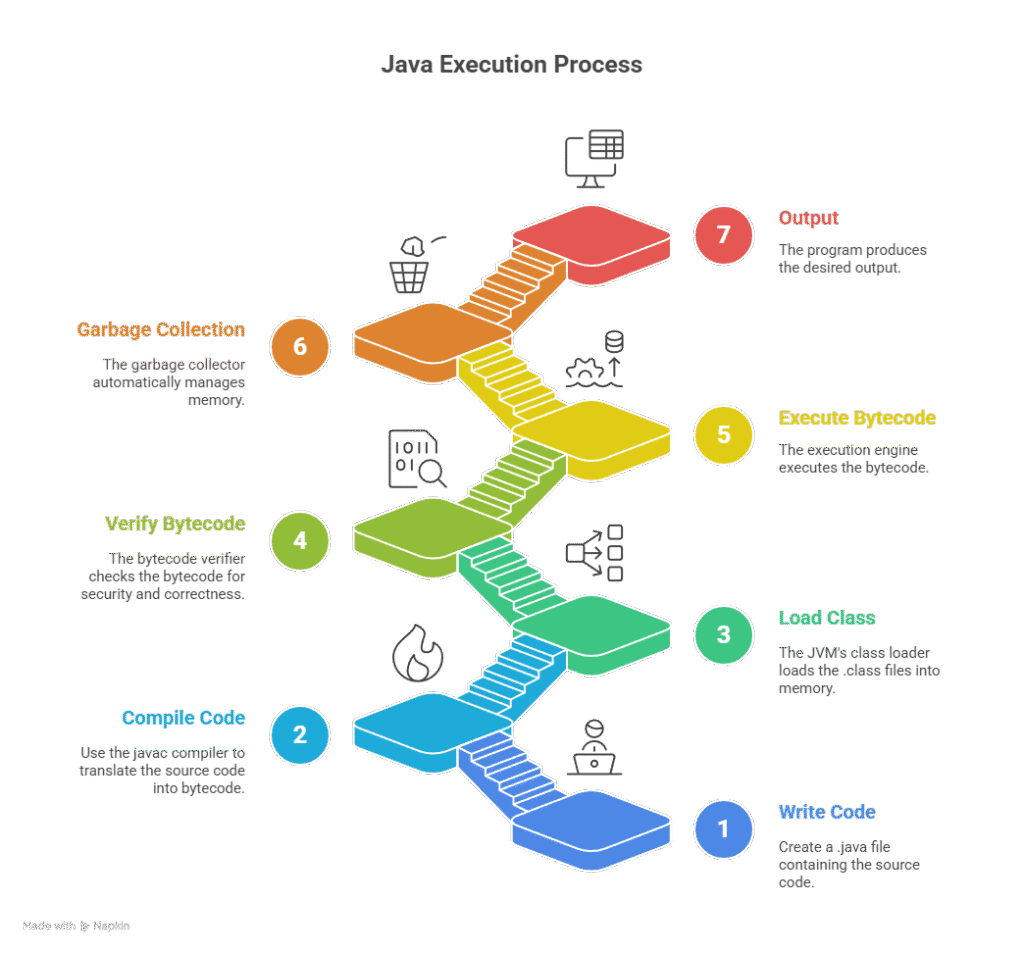
Java Execution Process (Introduction to Java)
The Java execution process includes 7 steps:
- Write Java Code: Create a .java file containing the source code.
- Compile the Code: Use the javac compiler to translate the source code into bytecode, generating .class files.
- Load the Class: The JVM’s classloader loads the .class files into memory.
- Verify the Bytecode: The bytecode verifier checks the bytecode for security and correctness.
- Execute the Bytecode: The execution engine (interpreter or JIT compiler) executes the bytecode.
- Garbage Collector: The garbage collector automatically manages memory.
- Output: The program produces the desired output.
Applications of Java Programming (Introduction to Java)
As we saw in the introduction to Java, there are too many applications of Java programming. In this article we will discuss some applications of Java programming.
Desktop Application:
Java can be used to design desktop applications. JavaFX, Swing, and AWT (Abstract Windowing Toolkit) are the APIs that do the work here. Using Java can have several benefits, such as platform independence, a rich set of libraries, strong community support, robust and secure object-oriented programming, multithreading support, scalability, integration capabilities, a mature ecosystem, and cross-platform compatibility.
Mobile Application Development:
In today’s technology and programming language era, it has been found that Java is the second most widely used language for designing mobile applications. Because Java is a cross-platform language, the applications built using it run effectively across mobile and other small-screen devices.
Web Applications:
Coming to web application development, Java is the perfect choice because of its ability to interact with a large number of systems. Components like JSP, web servers, Spring, and Hibernate make the web development process feasible.
Gaming Applications:
It supports Dalvik Virtual Machine and jMonkeyEngine, which provide an ace in building 2D and 3D Android games. Some popular games to be developed using it are Mission Impossible III, Minecraft, and Asphalt 6.
Also, it can be used to create artificial intelligence, big data technology, embedded systems, and cloud applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Java
From the introduction to Java till now, we can see that Java has been used in a large number of applications over the years. However, it has various advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages of Java:
- Platform independent: Java applications can be run on any device with a compatible Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
- Set of Inbuilt Libraries: Java provides a vast collection of prebuilt libraries and frameworks like Spring, Hibernate, and Apache Commons that accelerate the development process.
- Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) Support: Java provides object-oriented programming support. This nature promotes modularity, reusability, and easier maintenance of code through concepts like classes, objects, inheritance, polymorphism, and encapsulation.
- Security: Java is the most secure language in this language collection. It provides features like strong memory management (automatic garbage collection), exception handling, and type-checking. Its security features, including the absence of explicit pointers and a bytecode verifier, help reduce security risks.
- Multithreading: Java supports multithreading. This feature allows multiple parts of the program to execute concurrently. It reduces the CPU resources and improves application performance.
- Garbage Collector: Java provides a built-in garbage collector for memory management. It automatically deletes the objects that are no longer needed for the program or task.
Disadvantages of Java:
- Slower Execution Speed: It provides slower execution speed as compared to C and C++. Because it has a Java Virtual Machine (JVM) for the execution of the code, which added some extra layers of interpretation and translation.
- Lack of Low Level Access: As Java is designed to be more safe and secure, it restricts low-level access to system resources.
- Memory Consumption: It has Java Runtime Environment (JRE) and Garbage Collector. It can result in higher memory consumption as compared to the languages that allow more manual memory control.
Conclusion:
Java is one of the most reliable and widely used programming languages, and learning it can be a strong foundation for any student who wants to build a career in technology. In this Introduction to Java – A Complete Beginner’s Guide to Programming in Java, we explored the basics that every learner should know before moving on to advanced concepts.
The best way to understand Java is through consistent practice and real examples. Start with simple programs, strengthen your grasp of object-oriented principles, and then explore areas like database connectivity, web development, or Android applications. With dedication and patience, Java will not only improve your programming skills but also open doors to many opportunities in software development.
So, don’t wait – start your Java journey today and take the first step toward becoming a confident programmer.
